Intent
St Michael’s Computer Science department strives to equip our pupils for life after school by encouraging them to learn the fundamentals of both computer science and IT. The department creates resilient learners who can be challenged and stretched. This enables pupils to choose which pathway they would like to take throughout their education and beyond. As a department, we are committed to the safe use of the computer and developing their creativity and knowledge.
Implementation
In computing at KS3, we implement a blended curriculum with schemes of work that focus on both computer science and IT to improve the engagement of our learners. This allows most of them to choose their own pathway in KS4 but also how to stay safe whilst doing so. Our schemes of work feed into one another where the same computational concepts will be used throughout each unit so that learners deepen their understanding. This goes for all learners, as we aim to be as inclusive as possible and, therefore, differentiate our schemes of work to suit their needs. Moreover, through these differentiated units and STAR challenges, we are able to stretch our more able students. At KS3, during each unit, learners will test their knowledge with a midpoint assessment that they can improve once feedback has been given. This is done at the end of each unit with an end of unit test or portfolio-based project. These assessments feed into KS4, as quality assurance activities are undertaken to rigorously review what knowledge is needed at KS4 to help inform what learners will do at KS3. As KS4 is based on the pathway they take, learners will have regular end of topic assessments for computer science and IT, but a heavy focus will be coursework that is explored through portfolio based units at KS3 to ensure learners make the best possible progress.
Impact – KS3
By the end of KS3, pupils will have experienced the fundamentals of both computer science and IT. Pupils will learn how to think like a computer in order to complete the tasks set in all units. Pupils will be able to understand several key algorithms, how they are formed and how they can be related to real-world problems. Additionally, pupils will acquire a lot of technical language that enables them to explain the keywords and definitions that are present throughout the KS4 Computer Science and IT qualifications. These keywords will be learnt through practical lessons where pupils will acquire skills on how to use multiple software platforms. These activities will enable pupils to undertake creative projects where they can select, use and combine multiple applications. Furthermore, pupils will be exposed to more than one programming language, giving them the confidence to solve computational problems and develop their own programs of which they can be proud. Throughout all of the above, pupils will learn how to stay safe when using technology and how to report concerns if they arise.
Impact – KS4
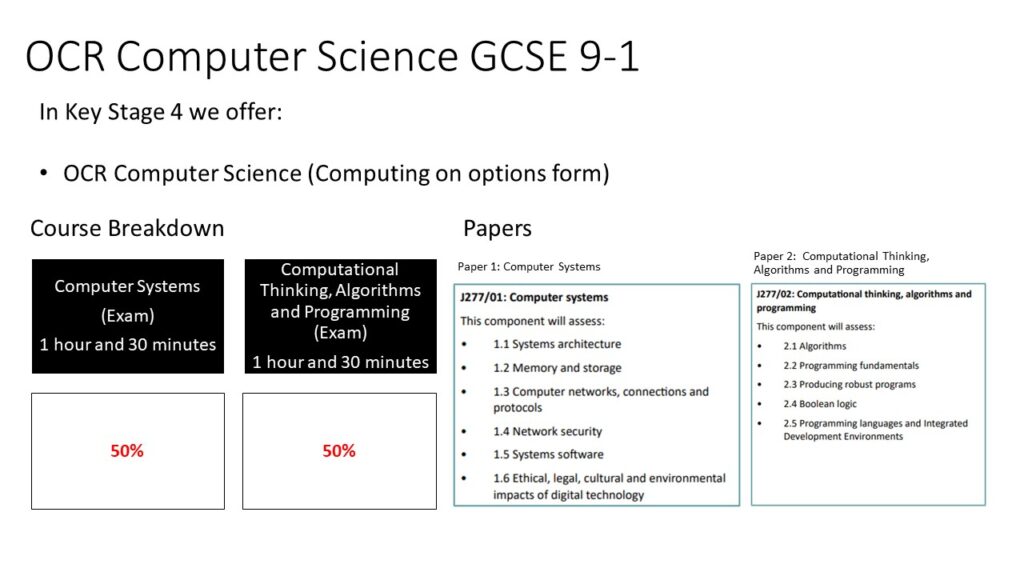
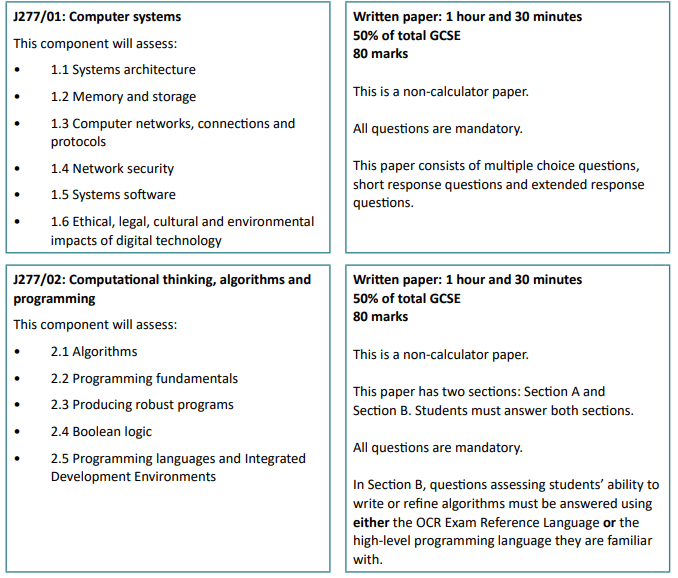
Computer Science
By the end of KS4, pupils will be capable of applying their analytic, problem-solving and computational thinking skills to enable them to provide responses to examination questions and through practical means when programming. Pupils will acquire technical language that will help them understand how a computer works in terms of how the data goes in and out of the computer and how it is processed. What pupils learn during KS3 and KS4 will prepare them and give them the confidence to engage effectively with computer science, both professionally and personally, if they wish.
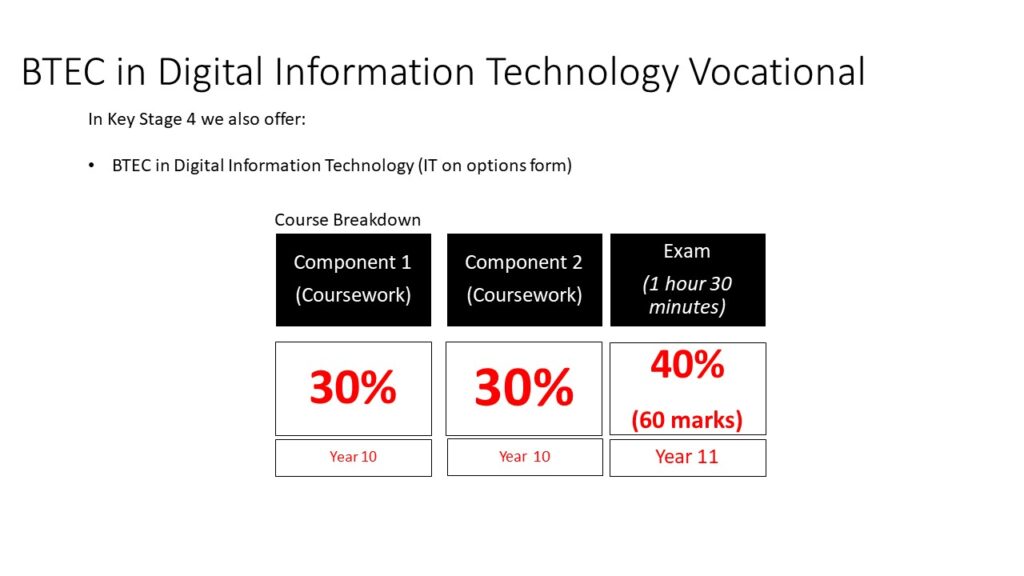
IT
By the end of KS4, pupils’ creativity will be stimulated by IT where they will be able to analyse and evaluate different computing devices, programs and applications to help inform their design decisions when creating their own, based on a scenario provided to them. They will also be able to answer questions related to these topics to show their understanding of how Information Technology is used by different demographics in different situations. What pupils learn at KS3 and KS4 will prepare them and give them the confidence to engage effectively with Digital Information Technology, both professionally and personally, if they wish.